The recent outbreak of Covid-19 leading to lockdowns in cities across the world has impacted all. Apart from companies dealing with physical goods, technology companies too are impacted with their facilities shut down and workforce directed to work from home.
In this scenario, tech startups are more agile than large enterprises. Tech startups depend less upon on premise data centres and can easily get their staff to connect from their homes and continue working.
So what are the options available to enterprise companies and their employees? Employees within a project need a common digital platform to work on wherever they are.
With AWS Cloud one is well aware that servers can be easily spun up and applications installed. In the case of firms in highly regulated verticals or with legacy workloads on legacy hardware running on premises, it may not be possible to do so.
There is also the fear related to potential malware and exploits running on unsecured home laptops and desktops.
The below factors which need to be taken into consideration can be factored in by using the various AWS services available-
- Consistency- Can a same platform be made available to employees working across a wide variety of devices and Operating Systems.
- Availability- With a huge load of all employees, can the system be available all the time.
- Performance- What will be the impact on the performance of the on premise firewall and internal systems
- Security- How can it be ensured that no malware or exploits is opened up. How will the client data be secured from being exported locally.
- Scalability- Can the platform be scaled appropriately to handle more or less users.
Based on the needs of the project and the role of the employee, users can be provisioned with an on cloud VDI or a remote desktop which in turn can be connected to the on premises systems.
The hardware requirements for end user devices to connect to such VDI options is minimal with a netbook on lease can be sufficient for temporary use.
Common Setup
The first step is to create a VPC and sub nets with CIDR block which will not conflict with the on premise network. A site to site VPN can be set up after obtaining the Public IP of the Customer Gateway (CGW) which is at the on-premise network.
AD Connector needs to be setup and used so that your on premise Active Directory can be used as a source of trust to authenticate your employees to provide access to applications and servers in AWS.
Then the recently launched Transit Gateway can be leveraged to establish connectivity between the VPC and the Site to Site VPN. Charges incurred for data transferred through it, are lower than charges for data transferred over the internet such as through a client to site VPN. AWS Client VPN can also be used to terminate VPN connections from multiple employees working remotely and getting connected to an AWS VPC and who through a bastion host can then access other instances and on premise servers.
SAP GUI on AWS
A large manufacturing customer of Sonata due to lockdown faced a challenge for their end users who needed to access the SAP GUI. While their SAP environment was on AWS and on-premises, many of their users still needed access to it through SAP GUI on local computers and local networks, which created a few challenges.
Users connecting remotely to their office, were running SAP GUI on their local desktops in their office and moving large amounts of data to and from the SAP environment on AWS were experiencing higher latency and a slow application experience. At the same time, SAP administrators still had to manage SAP GUI on-premises on each user’s computer to make sure everything is up-to-date with the latest security patches. So, while the SAP environment benefited from running on AWS, there were ways to further improve the users’ experience by running SAP GUI on AWS. This was done by leveraging the End User Computing options that AWS has available. SAP GUI was centrally managed and deployed as part of a common image across Amazon WorkSpaces and Amazon AppStream.
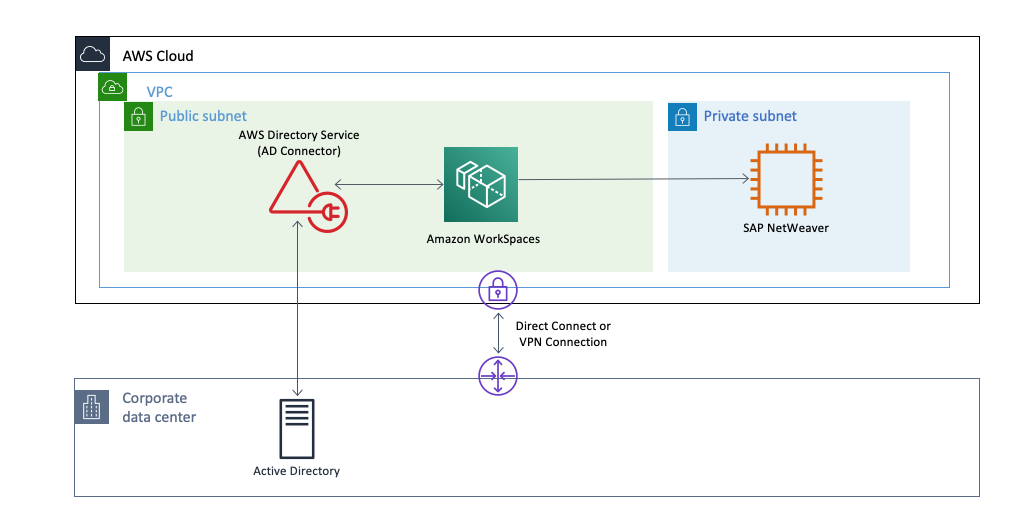
Because SAP GUI runs on AWS next to their SAP environment, the customer’s users didn’t need to upload or download data from AWS, and the application feels more responsive. At the same time, AppStream 2.0 makes it easier for the customer to manage SAP GUI for their users. With AppStream 2.0 there is central management of one version of SAP GUI and stream that exact version to every user. Users only access up-to-date versions of SAP GUI, and there is no need to deploy updates to every user’s computer. And, the applications run on AWS next to their data so nothing is stored on their users’ computers. Access restrictions were achieved, and user access management was done with existing Microsoft AD credentials. Finally, AppStream 2.0 is fully managed on AWS. This means AppStream 2.0 manages the AWS resources required to host and run the SAP GUI and related applications, scales automatically, and delivers the applications to the end users on-demand with simple pay-as-you-go pricing.
Amazon WorkSpaces
This service is used to provision workstations in AWS Cloud which can be securely accessed by using the Amazon WorkSpaces Client software which can be installed on a wide variety of Operating Systems. As only the display is delivered to the client and the compute is handled on AWS, there is reduced bandwidth requirements and latency. Also security is in built and a variety of controls can be leveraged to ensure there is no way for sensitive data and files to be exported from the WorkSpace to the end user system. WorkDocs is an add on that can be used to share folders and files among a set of employees internally without allowing malicious users access to the same. Common Workspace bundles can be used to provide a consistent setup for the employees. With Always On functionality which works out cheaper than other cloud providers, the availability and performance of a WorkSpace is not an issue and scalability can be handled both vertically and horizontally.
Amazon AppStream
This service can be leveraged to package only specific applications that are required to be accessed by the employees while working from home. These applications are then securely streamed through the browser to the end user device. Underlying infrastructure consists of fleets of instances. Consistency, Availability, Performance, Security and Scalability of these applications is not a challenge.
Amazon WorkLink
This service can be leveraged to provide secure mobile access to internal corporate websites and apps without the overhead of a VPN. The apps contents will get rendered as vector graphics securely in a container within AWS. Thus protection of highly regulated data can be ensured and also access to internal tools such as Jira and Confluence can be achieved.
Another VDI Option
In addition to this for those employees with desktops running within the enterprise and who only require access to them, a set of t2.micro instances running Windows can be spun up in the VPC and configured with SSH and RDP tunneled through SSH. These instances will act as bastion hosts. The users can then SSH and RDP to these bastion hosts. As Site to Site VPN from AWS to the on premise network has been setup and the Transit Gateway is attached to both the VPC and the VPN connection, once the on premise network administrator permits access to the specific VLAN, the user can then run an RDP session from the bastion host to his on premise desktop. Through Group Policies the controls required can be applied to the RDP session.
Thus Consistency, Availability, Performance, Security and Scalability is taken care of in all these solution options. With Wavelength coming up this could be integrated to further reduce the latency for employees who access VDI from a 5G connection.
About Sonata
Sonata Software Limited follows the Cloud Platformation™ Approach encompassing Consistency, Availability, Performance, Security, Scalability to bring about a digital transformation for its customers across the globe. This is backed by its teams comprising of several skilled and certified architects and engineers providing solutions and support to customers on AWS Cloud.